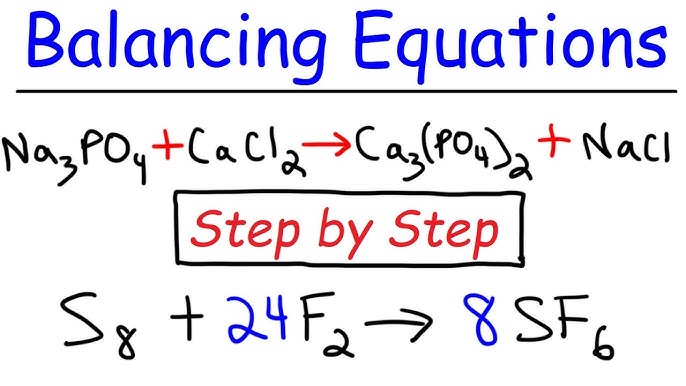
Introduction: Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill in chemistry that allows scientists to describe chemical reactions accurately. Whether you’re a student learning the basics of chemistry or a seasoned researcher analyzing complex reactions, understanding how to balance chemical equations is essential for predicting reaction outcomes and understanding chemical behavior. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the step-by-step process of balancing chemical equations, covering everything from identifying reactants and products to applying the principles of conservation of mass and charge, with practical tips and insights along the way.
Part 1: Understanding Chemical Equations and Stoichiometry
- Introduction to Chemical Equations: Chemical equations are symbolic representations of chemical reactions, showing the reactants on the left side and the products on the right side. Each chemical species is represented by its chemical formula, and the coefficients indicate the relative amounts of reactants and products.
- Stoichiometry Basics: Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It involves balancing equations, determining reaction stoichiometry, and calculating reactant and product amounts.
Part 2: Identifying Reactants and Products
- Recognizing Chemical Species: Identify the chemical species involved in the reaction, including reactants and products. Determine the chemical formulas of each species based on their elemental composition.
- Writing Chemical Equations: Write the chemical equation for the reaction, representing the reactants on the left side and the products on the right side. Ensure that the chemical formulas are correct and balanced, with appropriate subscripts and coefficients.
Part 3: Applying Conservation Principles
- Conservation of Mass: Balancing chemical equations involves applying the principle of conservation of mass, which states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. The total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products.
- Conservation of Charge: In addition to mass, chemical equations must also satisfy the principle of conservation of charge. The total charge of reactants must equal the total charge of products, accounting for the transfer of electrons in ionic reactions.
Part 4: Balancing Chemical Equations
- Start with the Most Complex Compound: Begin balancing the equation by adjusting coefficients for the most complex compound or species in the reaction. Balance elements that appear in only one reactant and one product first.
- Adjusting Coefficients: Use coefficients to balance the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. Start with elements that appear in multiple compounds and balance them one at a time, ensuring that the total number of atoms is equal on both sides.
- Using Trial and Error: Experiment with different coefficients to achieve balance in the equation. Adjust coefficients incrementally and systematically, checking the balance of each element after each adjustment.
Part 5: Verifying and Refining
- Check for Balance: Verify that the equation is balanced by counting the number of atoms of each element on both sides. Ensure that the total mass and charge are conserved and that all coefficients are in the simplest whole-number ratio.
- Refine as Needed: Refine the coefficients further if necessary to achieve the simplest and most balanced equation possible. Use common multiples to simplify coefficients and ensure that the equation is clear and concise.
Part 6: Practice and Application
- Practice Problems: Reinforce your understanding of balancing chemical equations by practicing with a variety of problems and reactions. Start with simple reactions and gradually progress to more complex scenarios.
- Real-World Applications: Apply your knowledge of balancing chemical equations to real-world scenarios, such as industrial chemical processes, environmental reactions, and biological pathways. Analyze reaction stoichiometry and predict reaction outcomes based on balanced equations.
Conclusion
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill in chemistry that requires practice, patience, and attention to detail. By following the comprehensive guide outlined above, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and techniques to balance chemical equations effectively and accurately. Remember to apply the principles of conservation of mass and charge, start with the most complex compounds, and refine coefficients systematically to achieve balance. With dedication and proficiency, you can master the art of balancing chemical equations and gain a deeper understanding of chemical reactions and their significance in the world around us.