Conducting performance reviews is a critical aspect of effective performance management in any organization. Performance reviews provide an opportunity for managers to evaluate the performance of their employees, provide feedback on strengths and areas for improvement, and set goals for future growth and development. Done well, performance reviews can motivate employees, enhance productivity, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore strategies, best practices, and tips for conducting performance reviews effectively, whether you’re a manager, team leader, or HR professional.
Understanding Performance Reviews:
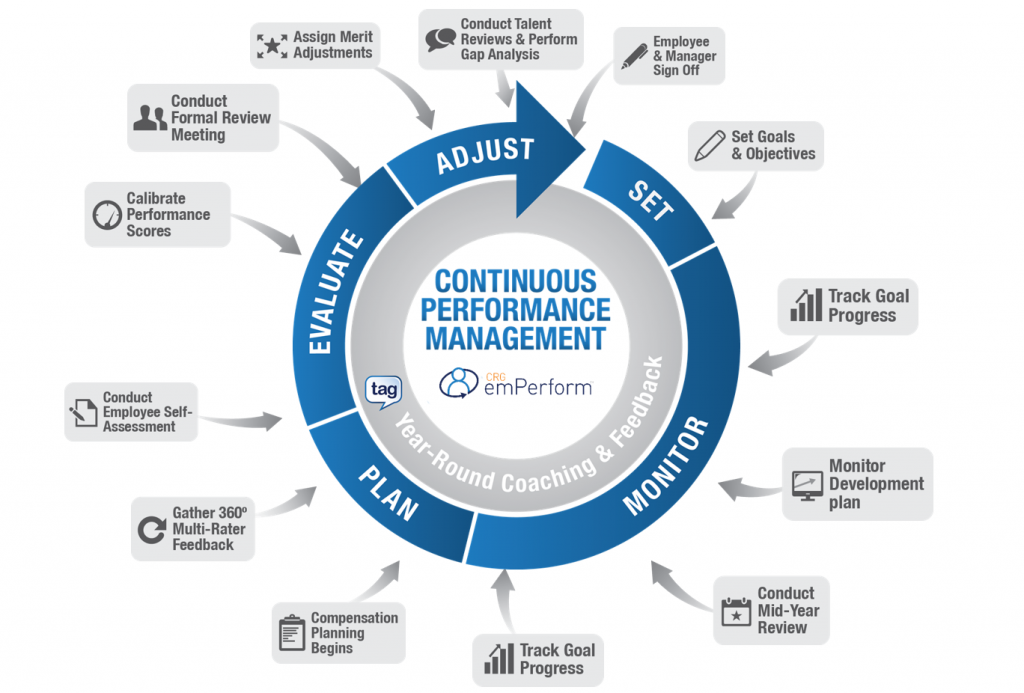
Performance reviews, also known as performance appraisals or evaluations, are formal assessments of an employee’s job performance over a specific period. They typically involve a structured discussion between the employee and their manager to review past performance, discuss accomplishments and challenges, and set goals for the future. Performance reviews may cover various aspects of performance, including job responsibilities, goals, competencies, and behaviors.
Key Objectives of Performance Reviews:
- Assess Performance: Evaluate the employee’s performance against established goals, objectives, and expectations. Identify areas of strength and areas for improvement based on performance metrics and feedback.
- Provide Feedback: Offer constructive feedback on the employee’s performance, highlighting successes, accomplishments, and areas where improvement is needed. Be specific, objective, and actionable in your feedback.
- Set Goals and Expectations: Collaborate with the employee to set clear, achievable goals and expectations for the upcoming performance period. Align goals with organizational objectives and the employee’s career aspirations.
- Identify Development Needs: Identify opportunities for employee development and growth, such as training, coaching, mentoring, or job rotations. Support the employee in developing new skills and competencies to enhance their performance and career prospects.
- Improve Communication: Enhance communication and collaboration between managers and employees by providing a forum for open, honest dialogue about performance expectations, feedback, and career development.
Strategies for Conducting Performance Reviews:
- Prepare Thoroughly: Before the performance review meeting, gather relevant data and documentation, such as performance metrics, project feedback, and previous performance reviews. Review the employee’s goals, objectives, and job responsibilities to provide context for the discussion.
- Schedule Adequate Time: Allocate sufficient time for the performance review meeting to ensure a thorough and meaningful discussion. Avoid scheduling other meetings or interruptions during the review to allow for focused attention.
- Create a Positive Environment: Set a positive and supportive tone for the performance review meeting. Begin by acknowledging the employee’s contributions and expressing appreciation for their hard work and dedication.
- Focus on Specific Examples: Provide specific examples and evidence to support your feedback, both positive and constructive. Use data, metrics, and examples from the employee’s work to illustrate your points and make feedback more tangible.
- Encourage Two-Way Dialogue: Encourage the employee to share their perspective on their performance, strengths, challenges, and career aspirations. Listen actively, ask open-ended questions, and be receptive to their input and feedback.
- Set SMART Goals: Collaborate with the employee to set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals for the upcoming performance period. Ensure that goals are aligned with organizational objectives and the employee’s role and responsibilities.
- Document the Discussion: Take notes during the performance review meeting to document key points, feedback, and action items. Summarize the discussion and outcomes in a written performance review document for future reference.
- Follow Up and Monitor Progress: Follow up with the employee after the performance review meeting to ensure they understand their goals and expectations. Provide ongoing support, feedback, and coaching to help them achieve their objectives.
Tips for Conducting Effective Performance Reviews:
- Be Objective and Fair: Base your feedback and assessments on objective criteria and evidence, rather than personal biases or opinions. Treat all employees fairly and consistently in your evaluations.
- Be Timely: Conduct performance reviews on a regular basis, typically annually or semi-annually, to provide timely feedback and support employee development. Avoid delaying or postponing performance reviews, as this can undermine their effectiveness.
- Focus on Behavior and Performance: Focus on the employee’s behavior and performance, rather than personality traits or personal characteristics. Provide feedback on actions and outcomes that are within the employee’s control.
- Balance Positive and Constructive Feedback: Strike a balance between recognizing the employee’s achievements and providing constructive feedback on areas for improvement. Highlight strengths and successes, but also address areas where performance could be enhanced.
- Be Supportive and Encouraging: Approach performance reviews as a coaching opportunity to support the employee’s growth and development. Offer encouragement, guidance, and resources to help them succeed in their role.
- Be Open to Feedback: Be open to receiving feedback from the employee on your own performance as a manager. Create a culture of mutual respect and trust where feedback is welcomed and valued.
- Follow Up Regularly: Performance reviews should not be a one-time event but part of an ongoing dialogue between managers and employees. Follow up regularly to monitor progress, provide support, and adjust goals as needed.
Overcoming Common Challenges:
- Addressing Performance Issues: Address performance issues promptly and constructively during the performance review meeting. Focus on specific behaviors or outcomes that need improvement and work with the employee to develop a plan for addressing them.
- Handling Emotional Reactions: Be prepared to handle emotional reactions from employees during performance reviews, such as defensiveness or disappointment. Stay calm, empathetic, and focused on the facts, and avoid escalating conflicts.
- Managing Disagreements: If the employee disagrees with your feedback or assessment, listen to their perspective with an open mind and seek to understand their point of view. Find common ground and work together to find a resolution.
- Dealing with Remote Employees: Conducting performance reviews with remote employees can present additional challenges, such as communication barriers and technology issues. Use video conferencing tools and collaboration platforms to facilitate remote performance reviews and ensure effective communication.
Conclusion:
Conducting performance reviews is a vital aspect of performance management that requires careful planning, communication, and collaboration between managers and employees. By following the strategies, best practices, and tips outlined in this guide, managers can conduct performance reviews effectively, provide valuable feedback and support, and help employees achieve their full potential. Remember that performance reviews are not just about evaluating past performance but also about setting goals for the future and supporting ongoing development and growth. With a proactive and constructive approach to performance management, organizations can create a culture of accountability, excellence, and continuous improvement.