Introduction:
In the world of genetics and biotechnology, CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing has emerged as a revolutionary tool with profound implications for medicine, agriculture, and beyond. This groundbreaking technology enables precise and efficient manipulation of DNA, offering unprecedented opportunities to study, treat, and potentially cure genetic diseases, modify organisms, and address global challenges. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the intricacies of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, its applications, implications, and the ethical considerations surrounding its use.
Understanding CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing:
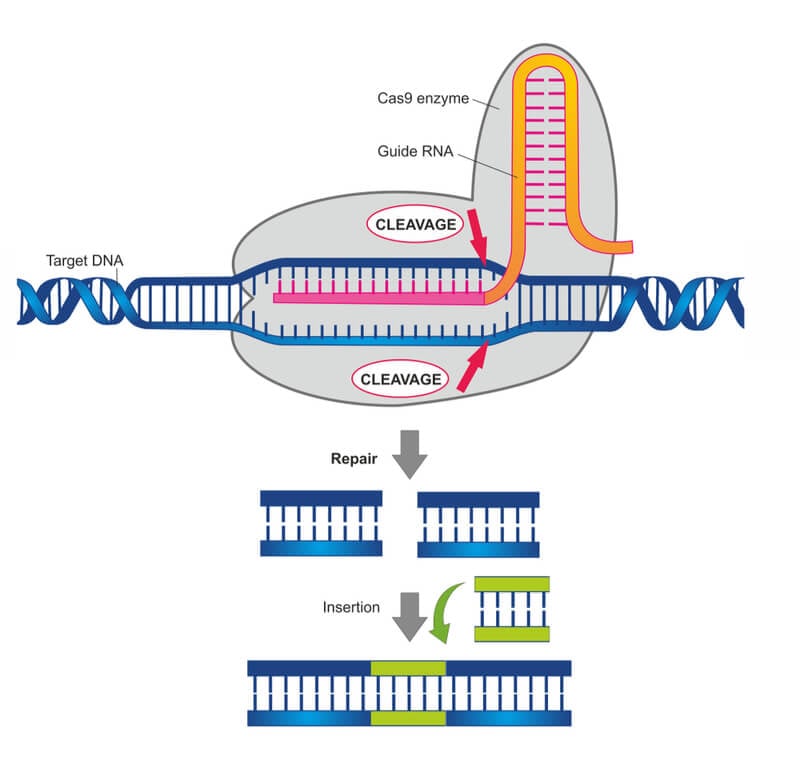
CRISPR-Cas9, short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9, is a naturally occurring system found in bacteria that serves as a defense mechanism against invading viruses. Scientists harnessed this system and repurposed it into a powerful gene editing tool. The CRISPR-Cas9 system consists of two main components: the Cas9 protein, which acts as molecular scissors, and a guide RNA (gRNA), which directs Cas9 to specific target sequences in the DNA.
The process begins with the design of a gRNA that matches the target DNA sequence of interest. The gRNA is then combined with the Cas9 protein and introduced into the target cells or organisms. Once inside the cell, the Cas9-gRNA complex binds to the target DNA sequence and induces a double-strand break (DSB) at that location. The cell’s natural repair mechanisms then kick in, leading to either non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), which can result in random insertions or deletions, or homology-directed repair (HDR), which allows for precise editing by providing a template DNA sequence.
Applications of CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing:
The versatility and precision of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing have led to a myriad of applications across various fields:
- Medical Research and Therapeutics: CRISPR-Cas9 has revolutionized the study and treatment of genetic diseases by enabling targeted modifications of disease-causing genes. Researchers are exploring its potential for treating disorders such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and muscular dystrophy.
- Agricultural Biotechnology: CRISPR-Cas9 offers new opportunities for crop improvement, disease resistance, and enhanced nutritional content in plants. It has the potential to address food security challenges by developing crops that are more resilient to environmental stressors and pests.
- Animal Models and Biomedical Research: CRISPR-Cas9 allows for the creation of genetically modified animal models for studying human diseases and developing new therapeutic approaches. It has facilitated advances in areas such as cancer research, neuroscience, and regenerative medicine.
- Microbial Engineering: CRISPR-Cas9 has been used to engineer microbes for various applications, including biofuel production, environmental remediation, and the production of pharmaceuticals and industrial chemicals.
- Human Germline Editing: Although highly controversial, CRISPR-Cas9 holds the potential for editing the human germline, which would allow for heritable genetic modifications. This raises ethical and safety concerns but also opens up possibilities for preventing hereditary diseases and enhancing human traits.
Implications and Ethical Considerations:
While CRISPR-Cas9 holds immense promise, it also raises important ethical, social, and regulatory considerations:
- Off-Target Effects: One of the challenges of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing is the potential for off-target effects, where unintended mutations occur at sites similar to the target sequence. Minimizing off-target effects is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficacy of gene editing therapies.
- Germline Editing: The prospect of editing the human germline raises ethical questions about the potential for unintended consequences, heritable genetic changes, and the implications for future generations. There is ongoing debate about the ethical and regulatory frameworks needed to govern germline editing.
- Equity and Access: There are concerns about equity and access to CRISPR-Cas9 technologies, particularly in healthcare. Ensuring equitable distribution of gene editing therapies and addressing disparities in access to treatment are important considerations.
- Regulatory Oversight: There is a need for robust regulatory oversight of CRISPR-Cas9 technologies to ensure responsible and ethical use. Regulatory agencies worldwide are grappling with how to balance innovation with safety and ethical considerations.
- Social and Cultural Impacts: CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing has broader social and cultural implications, including questions about human enhancement, identity, and the definition of “normalcy.” It raises philosophical questions about the nature of genetic determinism and the boundaries of human intervention in nature.
Conclusion:
CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing represents a paradigm shift in genetics and biotechnology, offering unprecedented opportunities to study, treat, and potentially cure genetic diseases, modify organisms, and address global challenges. While the technology holds immense promise, it also raises complex ethical, social, and regulatory considerations that must be carefully navigated. As scientists, policymakers, and society at large grapple with the implications of CRISPR-Cas9, it is essential to approach its use with caution, responsibility, and a commitment to ethical principles. By fostering dialogue, collaboration, and thoughtful oversight, we can harness the transformative potential of CRISPR-Cas9 while ensuring that its benefits are realized ethically and equitably for the betterment of humanity.