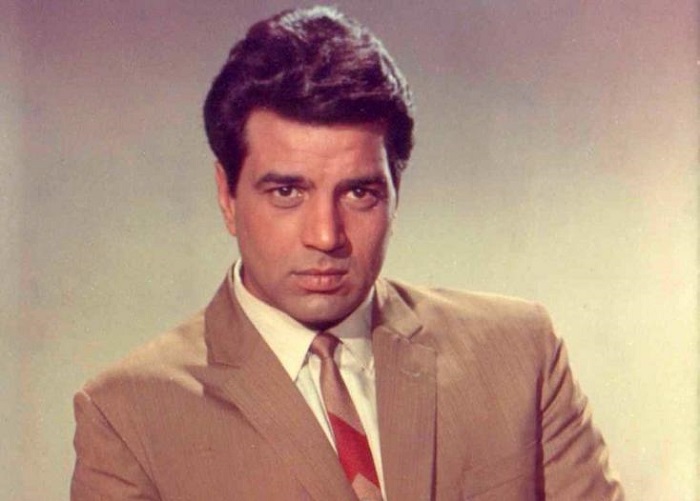
In the realm of Indian cinema, where stars shine bright and stories captivate millions, Dharmendra stands as a towering figure, revered and adored by generations of film enthusiasts. With his charismatic presence, versatile performances, and enduring appeal, Dharmendra has left an indelible mark on Bollywood, earning him a place among the pantheon of legendary actors. In this extensive exploration, we delve into the life, career, and legacy of Dharmendra, tracing his journey from humble beginnings to becoming one of the most beloved icons of Indian cinema.
Early Life and Background:
Born on December 8, 1935, in the village of Nasrali in Punjab, India, Dharmendra Singh Deol was raised in a modest household. His father, Kewal Kishan Singh Deol, was a school headmaster, and his mother, Satwant Kaur, instilled in him values of hard work, integrity, and resilience. Growing up in post-independence India, Dharmendra faced the challenges of rural life but harbored dreams of making it big in the world of entertainment.
Rise to Stardom:
Dharmendra’s journey to stardom began with his foray into acting, propelled by his striking looks, innate talent, and determination to succeed. After winning the Filmfare New Talent Award in 1960, he made his debut in the Hindi film industry with the film “Dil Bhi Tera Hum Bhi Tere.” However, it was his breakthrough performance in the 1966 film “Phool Aur Patthar” that catapulted him to fame and established him as a leading actor in Bollywood.
Iconic Roles and Memorable Films:
Throughout his illustrious career spanning over six decades, Dharmendra mesmerized audiences with his versatility, portraying a wide range of characters across genres. From intense dramas to lighthearted comedies, he effortlessly transitioned between roles, leaving an indelible impression on viewers. Some of his most iconic films include:
- Sholay (1975): Regarded as one of the greatest Indian films of all time, “Sholay” featured Dharmendra in the role of Veeru, a lovable rogue with a heart of gold. His chemistry with co-star Amitabh Bachchan and iconic dialogues from the film have become etched in the annals of Bollywood history.
- Mera Gaon Mera Desh (1971): In this action-packed drama, Dharmendra delivered a powerful performance as a vigilante seeking justice in a rural setting. The film showcased his ability to portray complex characters with depth and conviction.
- Yaadon Ki Baaraat (1973): Dharmendra captivated audiences with his portrayal of Shankar, a man on a quest for vengeance in this iconic musical drama. The film’s memorable soundtrack and Dharmendra’s charismatic presence contributed to its enduring popularity.
- Satyakam (1969): In this critically acclaimed drama, Dharmendra delivered a nuanced performance as Satyapriya, a man of integrity navigating the complexities of post-independence India. His portrayal earned him widespread acclaim and cemented his reputation as a versatile actor.
Personal Life and Legacy:
Beyond the glitz and glamour of the silver screen, Dharmendra’s personal life has also been the subject of public fascination. He married fellow actress Hema Malini in 1979, and their union has endured through the decades, symbolizing love and companionship in an industry known for its fleeting relationships. Dharmendra’s sons, Sunny Deol and Bobby Deol, have followed in their father’s footsteps, carving out successful careers in Bollywood.
As a testament to his enduring popularity and contributions to Indian cinema, Dharmendra has been honored with numerous awards and accolades, including the prestigious Filmfare Lifetime Achievement Award. His influence extends far beyond the realm of acting, as he continues to inspire aspiring actors and filmmakers with his humility, passion, and dedication to his craft.
In conclusion, Dharmendra’s journey from a small village in Punjab to the pinnacle of Bollywood stardom is a testament to the power of talent, perseverance, and resilience. Through his iconic performances, memorable characters, and timeless films, he has left an indelible legacy that will continue to inspire and entertain audiences for generations to come. Dharmendra, the legendary icon of Bollywood cinema, will forever hold a special place in the hearts of millions, reminding us of the magic and allure of Indian cinema.