Introduction:
Setting goals is an essential component of achieving success in any endeavor, and in the realm of business, the process becomes even more critical. SMART goals provide a structured framework for businesses to define objectives, clarify expectations, and drive performance towards desired outcomes. In this extensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of setting SMART business goals, providing readers with a comprehensive toolkit to navigate strategic planning with precision and confidence.
Understanding SMART Business Goals:
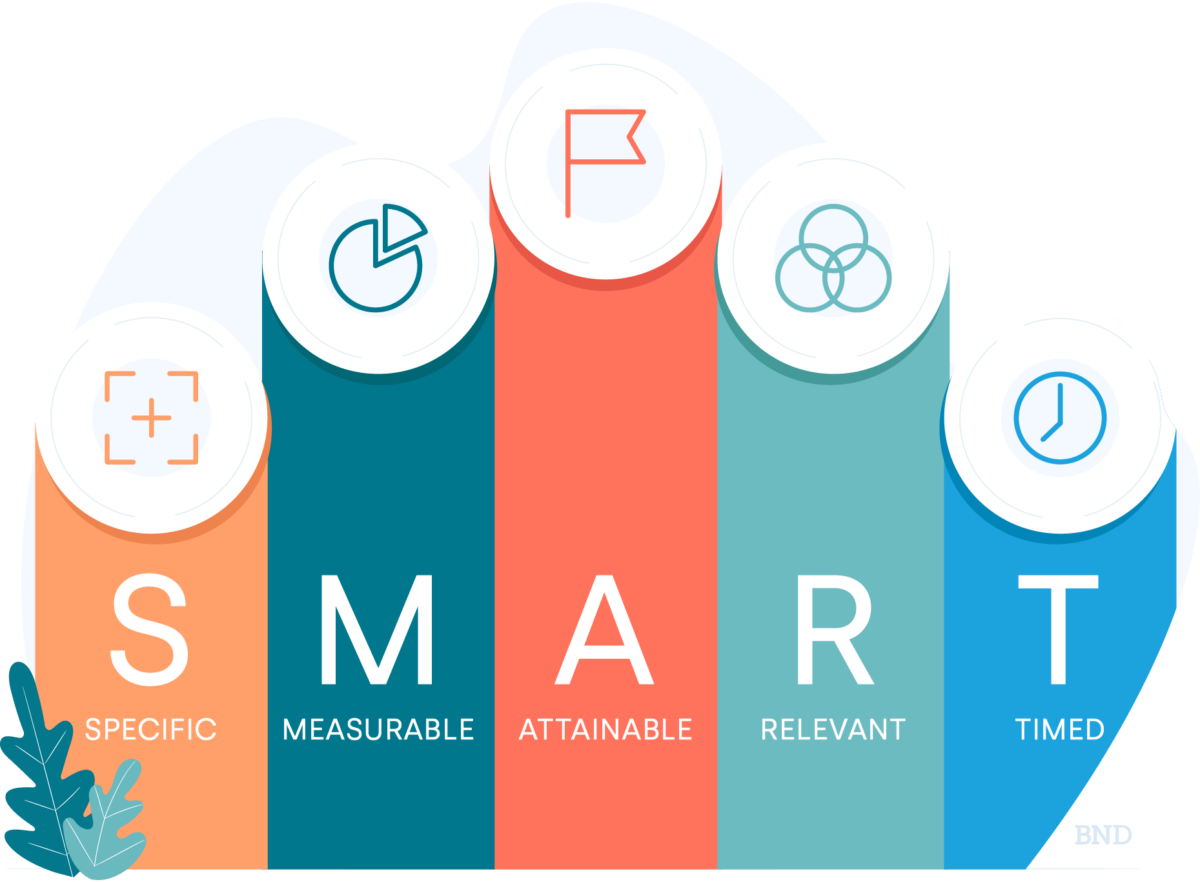
Before delving into the process of setting SMART goals, it’s crucial to understand the concept and principles behind the SMART framework. SMART is an acronym that stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. These criteria serve as guiding principles for setting goals that are clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with organizational objectives, and bounded by a defined timeframe. By adhering to the SMART criteria, businesses can ensure that their goals are actionable, trackable, and conducive to driving progress and success.
Components of SMART Business Goals:
- Specific: Specific goals are clear, well-defined, and focused on a particular outcome. They answer the questions of what, why, and how, providing clarity and direction for goal attainment. Specific goals leave no room for ambiguity or misinterpretation, enabling stakeholders to align their efforts and resources towards achieving the desired outcome.
- Measurable: Measurable goals are quantifiable and objective, allowing progress to be tracked and evaluated over time. Measurable goals include specific criteria or metrics that indicate success or completion, enabling stakeholders to assess performance and make data-driven decisions. Measurable goals provide a basis for accountability and performance management, facilitating informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Achievable: Achievable goals are realistic and attainable within the constraints of resources, time, and capabilities. They challenge stakeholders to stretch their abilities and strive for excellence while remaining within the realm of feasibility. Achievable goals strike a balance between ambition and practicality, motivating stakeholders to pursue meaningful objectives without setting unrealistic expectations or creating undue stress.
- Relevant: Relevant goals are aligned with the broader mission, vision, and strategic priorities of the organization. They contribute to the overall objectives and add value to the business, ensuring that efforts are focused on activities that matter most. Relevant goals resonate with stakeholders, inspire commitment, and foster a sense of purpose and alignment towards shared objectives.
- Time-bound: Time-bound goals are anchored by specific deadlines or timeframes, providing a sense of urgency and accountability for goal attainment. They create a sense of momentum and drive towards action, preventing goals from languishing indefinitely and ensuring timely progress towards desired outcomes. Time-bound goals help prioritize tasks, allocate resources effectively, and maintain focus on achieving results within a defined timeframe.
Setting SMART Business Goals:
Now, let’s embark on a systematic journey to set SMART business goals:
- Identify Strategic Priorities: Begin by identifying the key strategic priorities and objectives of the business. These may include areas such as revenue growth, market expansion, customer acquisition, product development, operational efficiency, or employee engagement.
- Define Specific Objectives: Once strategic priorities are identified, translate them into specific objectives that are clear, concise, and actionable. Use the SMART criteria to ensure that objectives are specific in nature, providing clarity and focus on desired outcomes.
- Establish Measurable Metrics: Determine the metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure progress towards each objective. These metrics should be quantifiable, objective, and aligned with the desired outcomes, enabling stakeholders to track performance and evaluate success effectively.
- Assess Achievability and Realism: Evaluate the achievability and realism of each objective within the context of available resources, capabilities, and constraints. Ensure that goals are challenging yet attainable, motivating stakeholders to strive for excellence while maintaining a realistic perspective on what can be accomplished.
- Align with Relevance: Ensure that each goal is aligned with the broader mission, vision, and strategic priorities of the organization. Goals should contribute to the overall objectives and add value to the business, ensuring that efforts are directed towards activities that support the organization’s long-term success.
- Set Time-Bound Deadlines: Establish specific deadlines or timeframes for achieving each goal, creating a sense of urgency and accountability for goal attainment. Time-bound goals help prioritize tasks, allocate resources effectively, and maintain focus on achieving results within a defined timeframe.
- Communicate and Cascade Goals: Communicate SMART goals to all relevant stakeholders, ensuring alignment, understanding, and commitment towards shared objectives. Cascade goals throughout the organization, ensuring that each department, team, and individual understands their role in contributing to goal attainment.
- Monitor Progress and Adapt: Continuously monitor progress towards SMART goals, tracking performance against established metrics and deadlines. Identify any deviations or obstacles to goal attainment and adapt strategies or tactics as necessary to stay on track towards achieving desired outcomes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, setting SMART business goals is a fundamental aspect of strategic planning and organizational success. By adhering to the SMART criteria – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound – businesses can ensure that their goals are clear, actionable, and conducive to driving progress and success. Whether pursuing revenue growth, market expansion, operational efficiency, or employee engagement, SMART goals provide a structured framework for defining objectives, clarifying expectations, and driving performance towards desired outcomes. So dive into setting SMART goals today, unlock the full potential of your business, and chart a course towards sustainable growth and success with confidence and clarity.