Updating drivers is essential for ensuring optimal performance, compatibility, and stability of hardware components on your computer. Whether you’re using Windows, macOS, or Linux, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of updating drivers, understanding the importance of driver updates, and using tools to simplify the process.
Understanding Driver Updates
What are Drivers?
Drivers are software programs that allow your operating system to communicate with hardware devices such as graphics cards, sound cards, network adapters, and peripherals. They facilitate proper functioning and performance optimization of hardware components.
Importance of Updating Drivers
- Performance Optimization: Updated drivers often include performance improvements and bug fixes, enhancing the functionality of hardware.
- Compatibility: New drivers may add support for new features or improve compatibility with the latest software updates and operating system versions.
- Security: Driver updates can address security vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited by malicious software.
Types of Drivers
- Graphics Drivers: Manage graphics processing units (GPUs) for enhanced visual performance in games and multimedia applications.
- Audio Drivers: Control audio output and input devices, ensuring clear sound quality and compatibility with audio peripherals.
- Network Drivers: Enable network adapters to connect to the internet and local network, optimizing data transfer speeds and stability.
- Peripheral Drivers: Support printers, scanners, keyboards, mice, and other peripherals, ensuring they function correctly with the operating system.
How to Update Drivers: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Identify Drivers to Update
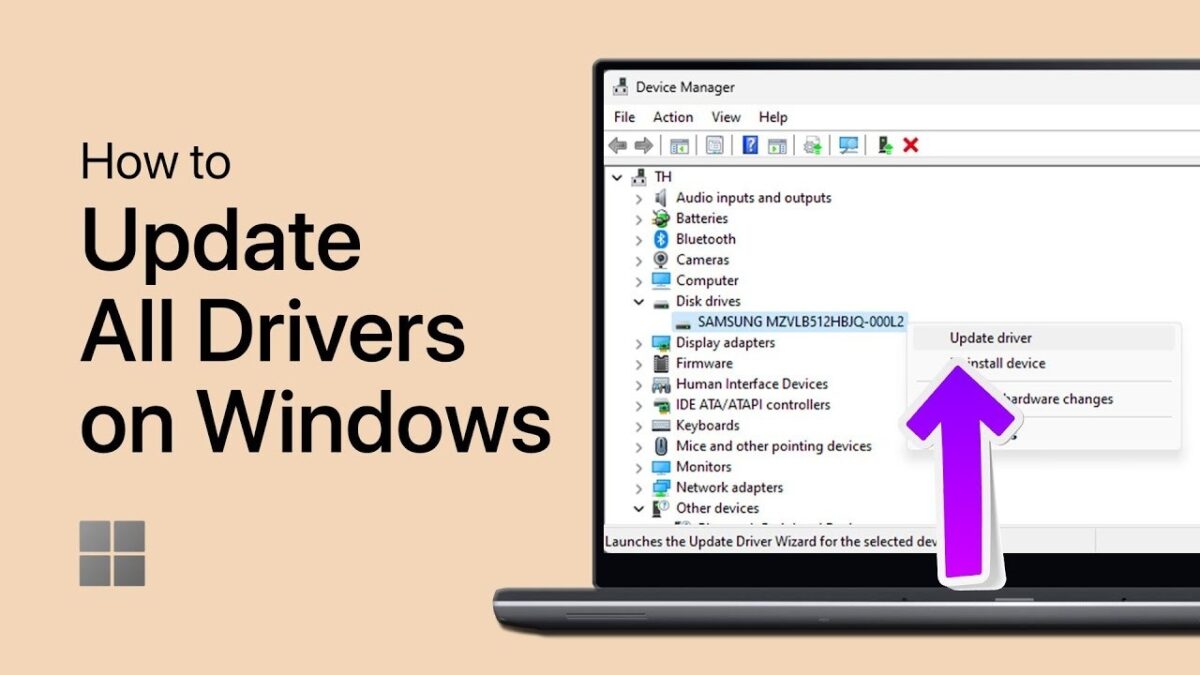
- Device Manager (Windows):
- Right-click on the Start menu and select “Device Manager.”
- Expand categories (e.g., Display adapters, Network adapters) to view installed hardware.
- Right-click on a device and select “Update driver” to check for updates.
- System Information (macOS):
- Click on the Apple menu > About This Mac > System Report.
- Navigate to Hardware > Graphics/Displays, Network, or other categories to view hardware details.
- Check manufacturer websites for driver updates.
- Package Manager (Linux):
- Use package managers like
apt,yum, ordnfdepending on your Linux distribution. - Use commands like
sudo apt-get updateandsudo apt-get upgradeto update all installed packages, including drivers.
- Use package managers like
Step 2: Update Drivers Using Manufacturer’s Website
- Visit Manufacturer’s Website:
- Go to the official website of the hardware manufacturer (e.g., NVIDIA, AMD, Intel).
- Navigate to the Support or Downloads section to search for the latest drivers for your specific hardware model and operating system.
- Download and Install Drivers:
- Download the latest driver package compatible with your hardware and operating system.
- Run the installer and follow on-screen instructions to install updated drivers.
Step 3: Use Driver Update Software (Optional)
- Third-Party Tools (Windows):
- Tools like Driver Booster, Driver Easy, or Snappy Driver Installer can automate driver updates.
- Download and install the software, scan your system for outdated drivers, and follow prompts to update them.
- macOS and Linux:
- Check for updates using built-in software update utilities or package managers.
- Some third-party tools may offer driver update functionalities, but they are less common and often unnecessary on macOS and Linux.
Step 4: Windows Update (Windows Only)
- Windows Update:
- Windows Update may automatically deliver updated drivers for hardware components.
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and click “Check for updates” to install available driver updates.
Step 5: Verify and Troubleshoot
- Verify Driver Installation:
- After updating drivers, restart your computer to apply changes.
- Open Device Manager (Windows), System Information (macOS), or check via terminal commands (Linux) to verify driver versions.
- Troubleshoot Issues:
- If encountering issues after updating drivers (e.g., performance problems, hardware malfunctions), roll back to previous driver versions via Device Manager (Windows) or reinstall the older drivers from manufacturer’s website.
Best Practices for Updating Drivers
- Regular Updates: Check for driver updates periodically to ensure hardware compatibility and performance.
- Backup Drivers: Before updating, create backups or restore points to revert changes if necessary.
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Follow manufacturer guidelines and instructions when updating drivers, especially for critical components like BIOS.
- Avoid Third-Party Tools (macOS and Linux): Use built-in utilities or official package managers to update drivers on macOS and Linux to avoid compatibility issues.
- Read Release Notes: Review release notes accompanying driver updates to understand improvements, fixes, and known issues.
Conclusion
Updating drivers is crucial for maintaining optimal performance, compatibility, and security of hardware components on your computer. By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing built-in tools, manufacturer websites, and optional driver update software, you can effectively update drivers on Windows, macOS, and Linux systems. Ensure to check for updates regularly, backup drivers before making changes, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise after updating drivers. If unsure about any steps or encountering technical challenges, consult manufacturer support, refer to online resources, or seek assistance from experienced professionals to update drivers effectively and enhance your computer’s performance and reliability.